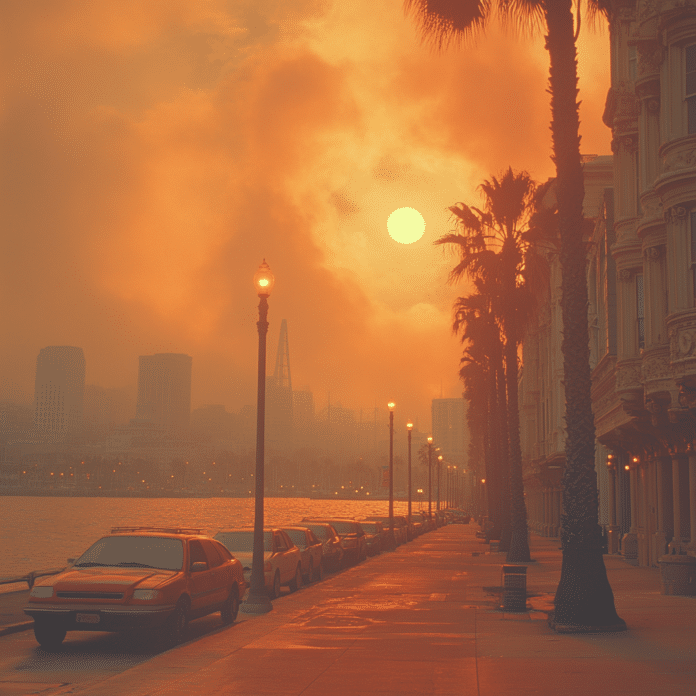
The Bay Area is currently experiencing a heat wave like never before, with bay area heat wave temperatures soaring to unprecedented heights this October. Historically, this time of year marks the transition into cooler autumn weather across Northern California, yet this month has shattered records with several areas reporting temperatures surpassing 100°F. The impact of these extreme conditions raises a multitude of concerns ranging from climate change implications to energy consumption and public health risks, a trifecta that has residents on edge.
The bay area heat wave temperatures can be attributed primarily to offshore winds that sweep in from the inland regions, driving up the heat as they hit the coastal zones. Meteorologists, including local experts like Mr. Flynn, are pointing to human-induced greenhouse gas emissions as the leading cause behind this alarming trend. The situation is further exacerbated by the fact that San Francisco, known for its temperate climate, recorded a staggering 97°F on October 1, 2024—smashing previous records set during the severe heat wave of 1980.
As temperatures climb, Bay Area cities are grappling with the fallout. From increased energy consumption to a spike in emergency room visits, the effects of this bay area heat wave are being felt across the community. Local public health officials are urging residents to stay hydrated and avoid strenuous outdoor activities, especially seniors and those with pre-existing health conditions. This October is setting a concerning precedent that demands our attention and action as we head deeper into the climate crisis.
Top 7 Record-Breaking Temperature Days in the Bay Area

Impact of Sierra Nevada California Snow Storm on Local Weather Patterns
While the Bay Area swelters, an intriguing contrast is taking place in the Sierra Nevada. As of October 20, 2024, a recent snowstorm has blanketed parts of the region in up to a foot of snow. This bizarre interplay of weather highlights the unpredictable nature of current climate patterns. Many residents are left scratching their heads, questioning how such extreme heat can coexist with early snowfall mere miles away.
Meteorologists attribute this phenomenon to shifting wind patterns influenced by larger climatic changes. It provides a stark reminder of how interconnected our weather systems are, complicating traditional forecasting models. Communities near the Sierra must prepare not just for heat but also for a potential dip into winter weather, making planning essential for local governments and residents alike.
The early snow advisory for the Sierra Nevada underscores an urgent call to action: communities need to adapt. As scientists continue to study these evolving weather patterns, it’s vital for state and local authorities to develop comprehensive strategies for managing both extreme heat and unpredictable cold fronts.
Global Comparisons: Weather Extremes in Puebla, Mexico and Southern California
The unusual weather patterns in the Bay Area reflect a broader, global trend of climate instability. In Puebla, Mexico, a recent hailstorm wreaked havoc in October, damaging agricultural sectors and disrupting local economies. Similar climate fluctuations can be noted in Southern California, where temperatures also soared, with Ventura County reporting highs of 102°F, raising concerns about wildfires in a region already susceptible to such disasters.
This climate chaos isn’t just a local issue; it’s a global emergency. As scientists observe these trends, the potential for crop failures, increased fire risk, and economic instability across regions invites urgent discussions about resilience strategies. Urban areas must collaborate to implement effective solutions that can mitigate the impacts of unpredictable weather.
Public Health Concerns: Rise of Dengue Fever in Pasco, Florida
Compounding these weather issues, health alerts from Pasco County, Florida, indicate a troubling increase in cases of dengue fever. Experts pinpoint that rising bay area heat wave temperatures, along with increased humidity, create ripe conditions for the proliferation of disease-carrying mosquitoes. Public health officials caution that these conditions are not just limited to Florida; rising temperatures enhance the likelihood of similar outbreaks in other regions.
The intersection of extreme heat and public health safety highlights the urgent need for preventive measures. Residents are urged to employ strategies like eliminating standing water and using insect repellent to combat these insidious threats. With the potential for such outbreaks rising, it’s crucial for communities to remain vigilant and proactive.
Preparing for Future Weather Patterns: Sierra Nevada Early Snow Advisory
Given the dramatic weather shifts, the Sierra Nevada has issued an early snow advisory, spotlighting the dual challenges of managing extreme temperatures and snowstorms. State officials emphasize that planning is key as climate extremes become the new standard. Residents must brace themselves not only for the immediate challenges of the heat wave but also for potential impending winter conditions.
As communities come to terms with this climatic rollercoaster, stakeholders are encouraged to engage in sustainable practices that address both environmental and public health needs. Educating residents about climate adaptation can significantly bolster community resilience as we face more unpredictable weather systems.
Innovative Strategies for Coping with Climate Extremes
In response to the bay area heat wave temperatures, municipalities are activating cooling centers to assist vulnerable populations impacted by excessive heat. These centers offer refuge equipped with air conditioning for those without adequate cooling options at home. Such initiatives exemplify how cities can mobilize resources to safeguard their communities.
California’s government is ramping up investments in renewable energy to ease the pressure on energy grids as more residents rely on air conditioning during extreme heat events. Creating a sustainable energy infrastructure is vital for long-term resilience.
As we navigate these weather extremes, collaboration among health, technology, and policy stakeholders can amplify efforts toward sustainability. The need for proactive urban planning is more pressing than ever as we look to integrate ecological considerations into future development.
From the sweltering heat waves in the Bay Area to hailstorms in Puebla and unsettlingly high temperatures in Southern California, these experiences should prompt a reevaluation of how we address climate challenges. There’s no time like the present to shift our focus from short-term fixes to long-lasting, sustainable solutions for protecting both our environment and communities in the face of an uncertain future.
Through sustained action and collaboration, we can address the pressing issues surrounding climate change and safeguard public health, ensuring a better tomorrow for all.
Bay Area Heat Wave Temperatures Break Records
Scorching Stats
This October, residents of the Bay Area aren’t just soaking up the sun; they’re dealing with record-breaking heat wave temperatures that have made history. This month alone has seen temperatures soar into the high 90s, some areas even edging closer to the century mark. With climate shifts causing unusual weather patterns, these high readings aren’t just a fluke—they’re part of a larger trend. Speaking of trends, did you know that Maryland state Taxes have seen significant changes too? Just like the weather, tax regulations have their ups and downs!
With all this heat, you might find yourself craving a refreshing drink. For many parents, finding just the right formula is key during these sweltering days. Enter Enfamil Gentlease, which offers a gentler option for babies who might get fussy in the heat. And, if you’re looking for exciting entertainment during those hot evenings, there’s buzz around a Snoop Dogg new movie that promises to be a fun diversion!
Weathering the Effects
Heat waves like this can put a real strain on infrastructure. Just last month, a major freight train experienced a derailment due to the extreme temperatures affecting the tracks. It’s a stark reminder that when the mercury rises, so do the risks. But there’s more than just freight in jeopardy— local sports teams are also feeling the heat. This month, game attendance surged for the Suns vs. Pacers matchup, likely powered by a desire to escape the soaring temperatures while cheering for the home team.
Interestingly, the rise in temperatures isn’t the only noteworthy aspect of October. Economic discussions surrounding properties reveal that understanding forms such as the 1098 mortgage interest statement can flush out better decision-making for potential homeowners. Residents might want to keep their cool while navigating fierce competition in the real estate market, just as fans hope to see standout performances on the court. And let’s not forget the culinary scene—places like Szechuan House offer spicy dishes that might just “heat” things up in more ways than one!
The Bigger Picture
As experts evaluate these unprecedented bay area heat wave temperatures, it’s clear that this is not just a fleeting event but a wake-up call. It’s essential to keep in mind the implications of these temperature spikes on our environment and daily lives. For instance, folks are starting to dig into discussions about the lasting net worth of celebrities like Jim Caviezel, discussing how even their wealth can be affected by fluctuating economies and weather patterns alike.
In a nutshell, this October heat wave is not just a local story; it’s a piece of a vast puzzle involving economics, civic responsibilities, and even pop culture. With figures like Conrad Chisholm leading the conversations around climate change, one can hope to foster awareness and find solutions. So, whether you’re enjoying a leisurely evening out or catching up on news, remember the temperature’s rising, and it’s time to keep those conversations going!

What caused the bay area heat wave?
This week’s heat wave in the Bay Area is due to offshore winds blowing from inland areas to the coast, which are pushing temperatures up significantly.
What was the hottest day in the Bay Area?
The hottest day ever recorded in the Bay Area was 106 degrees on September 1, 2017, while San Francisco hit 97 degrees on October 1, 1980.
What temperature is considered a heat wave?
A heat wave typically means two or more days of excessive heat, with the Northeast considering temperatures of 90°F or higher for three consecutive days as the threshold.
Why is it still so hot in September 2024?
It’s still hot in September 2024 mainly because of ongoing climate changes, along with human-induced greenhouse gas emissions that raise global temperatures.
Is California getting hotter?
Yes, California is getting hotter. Data from recent decades shows a clear upward trend in temperatures across the state.
What is really causing the heatwave?
The heatwave is primarily caused by human-induced greenhouse gas emissions, which trap heat in the atmosphere and contribute to rising global temperatures.
What is the hottest temperature ever recorded in the world?
The hottest temperature ever recorded in the world reached a staggering 134 degrees Fahrenheit in Furnace Creek Ranch, California, back in July 1913.
What is the hottest month in the Bay Area?
August usually holds the title for the hottest month in the Bay Area, but varying factors can shift that in any given year.
What is the hottest day in US history?
The hottest day in US history occurred on July 10, 1913, in Furnace Creek Ranch, California, hitting 134 degrees Fahrenheit.
Which state has the most heat waves?
Texas often experiences the most heat waves of any state in the U.S., thanks to its size and climate conditions.
What are the symptoms of body heat?
Symptoms of body heat can include excessive sweating, dizziness, fatigue, nausea, and confusion; it’s important to stay cool and hydrated.
How hot will heat waves be in 2050?
Heat waves in 2050 are predicted to be much hotter due to ongoing climate change, with scientists warning of severe heat exceeding current records.
What is the hottest year in the world?
The hottest year recorded globally was 2020, a part of a broader trend of increasing temperatures tied to climate change.
Why is Germany so hot in summer?
Germany experiences high summer temperatures due to a combination of weather patterns, climate change, and geographic factors that can elevate heat.
Which year is El Niño?
El Niño is a complex weather pattern that can happen every few years; its next significant occurrence is anticipated around 2026.
What was the hottest day in history in California?
California’s hottest day in history recorded during the heat wave was also in Furnace Creek Ranch, with temperatures soaring to 134 degrees in July 1913.
What was the hottest day in Berkeley?
Berkeley’s hottest day saw temperatures reaching 103 degrees, matching the intense heat that many areas faced during heat waves.
What is the record temperature in San Francisco?
San Francisco’s record temperature stands at 106 degrees, a scorching mark set during a hot spell in September 2017.
What was the highest warm day?
The highest warm day recently recorded reached 97 degrees in San Francisco on October 1, breaking old records for that date.
Why is there a heat dome over California?
A heat dome over California is caused by high-pressure systems trapping warm air near the surface, leading to prolonged high temperatures.
What is the main cause of an area becoming a heat island?
Heat islands form when urban areas replace natural land with concrete, asphalt, and buildings that absorb and retain heat, causing local temperatures to rise.
Why is the Bay Area so temperate?
The Bay Area is temperate due to its unique geography and maritime climate, which are influenced by the Pacific Ocean and the surrounding hills.
What caused the 1980 heat wave?
The 1980 heat wave was caused by a combination of high-pressure systems and dry conditions, which led to extremely high temperatures across the region.



